Waste heat: a key lever for decarbonizing industry: expert opinion piece
Recovering waste heat means reducing dependence on fossil fuels, improving the energy performance of industrial sites, and contributing to a virtuous local cycle. Focus on a concrete, profitable, and underutilized lever for decarbonization!
Waste heat, at the heart of industrial performance
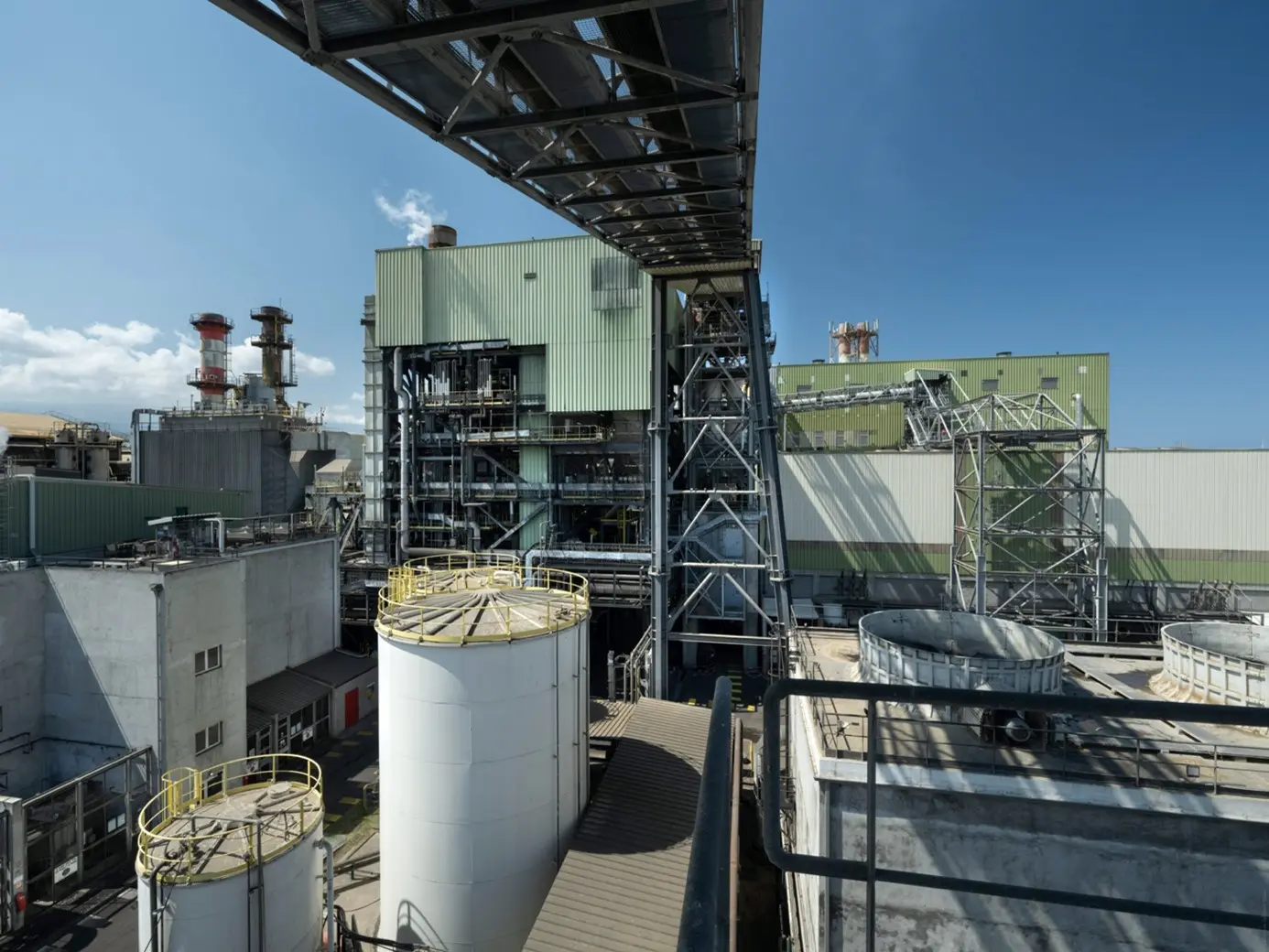
Waste heat, a by-product of industrial processes that is often overlooked, represents a largely untapped source of energy. In France, it accounts for 30% of the final energy consumption of French industry, equivalent to that of 20 million households. This heat, known as “waste heat” or “recovery heat” according to the definition of the Ministry of Energy Transition, can become a local carbon-free energy source for other processes and uses once it has been recovered. In concrete terms, this involves capturing the lost heat and then transporting and/or transforming it so that it can be used in another process or application, in thermal or electrical form. In a context of phasing out fossil fuels and reducing CO2 emissions, the recovery of waste heat is a major challenge for manufacturers, from large corporations to SMEs, with increasingly rational and circular use of energy, in line with their regulatory obligations and CSR objectives. Focus on the importance of carrying out a waste heat recovery project in accordance with best practices to create value and achieve sustainable decarbonization!
Expertise in energy efficiency is a must!
Relying on an expert partner in energy efficiency is crucial to the success of this type of project. In the most energy-intensive sectors, such as cement manufacturing, agri-food, metallurgy, and even paper manufacturing, industrial processes are often complex. It is necessary to verify the quality of the recoverable energy source, expressed in MWh, in order to valorize it and dedicate it to a new use. An in-depth energy diagnosis is required to understand the main energy vectors before taking action: electricity, cooling, water, compressed air, heating, and ventilation. It is also necessary to define clear objectives that will guarantee concrete results.
Depending on the level of involvement of the manufacturer, the partner must offer agile support that adapts to their organization, from project management assistance to project management and turnkey solutions. The aim is to choose the most appropriate support to determine the best recovery solution for each use, from financing to implementation. With more than 50 projects to its credit, E’nergys supports manufacturers in their “waste heat” projects, using a results-oriented approach, from the action plan to monitoring and continuous improvement!
The six key factors for a successful waste heat project!
The success of a waste heat project rests on six essential pillars. The manufacturer must be able to rely on a truly multidisciplinary project team combining technical expertise, management skills, and financial expertise. The project must have clear and measurable objectives, based on KPIs defined in advance in terms of energy savings and/or CO2 emissions. As a strategic project by nature, it also requires rigorous monitoring, secure upfront financing, and fluid internal communication to raise awareness and unite teams. Support from an expert such as E’nergys helps identify the “right” recovery solution between the available “useful” energy source and the manufacturer’s consumption needs.

Towards circular industrial energy!
Choosing to recover and utilize waste heat means initiating an industrial circularity approach—a new source for multiple uses—which offers numerous benefits and advantages. This type of project, which requires significant investment, can be made profitable and amortized in just a few years thanks to the energy savings achieved and the reduction in purchases of fossil fuels, whose prices are volatile. In fact, recovering waste heat allows manufacturers to consume it themselves as needed, for example to heat or cool their commercial spaces, or even to sell it to third parties, from other manufacturers to local authorities, thereby generating additional revenue. Beyond the economic benefits, waste heat recovery fits perfectly into a local energy loop at a time when energy production and distribution methods need to be rethought.
The waste heat ecosystem is booming!
More and more companies, from large corporations to SMEs, are committing to waste heat recovery in order to reduce their carbon footprint. The dynamism of this sector is illustrated by the rise of start-ups in this field: according to BPI, more than 30% of industrial start-ups are already positioning themselves in this area. In order for French manufacturers to make the most of this energy—a third of which is still lost according to ADEME—it is imperative to find and exploit the “right” source according to actual consumption needs, with complete agility and efficiency!







